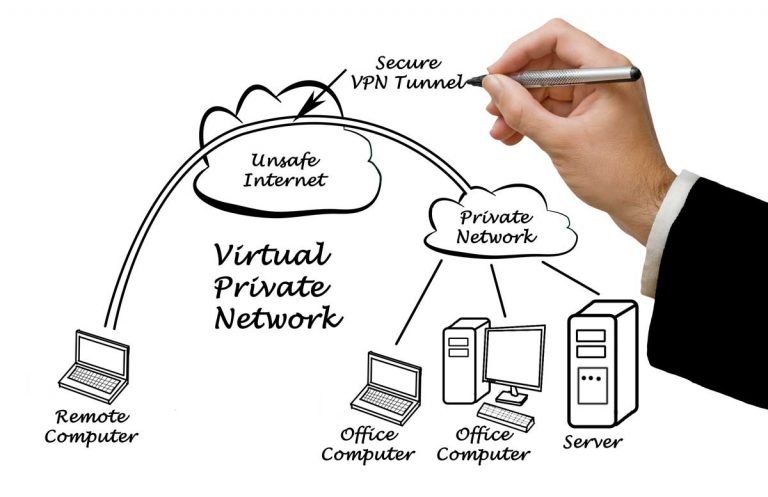
Virtual Private Networks, also called VPNs, aren’t new. The role of VPNs is to enable communication between networks or between networks and individual computers. VPNs establish secure connections over public networks such as the internet in order to transmit data between two points. For example, a consultant traveling in Asia may connect via a VPN to his company’s headquarters in Austin, TX in order to print out a document for a co-worker from his laptop. VPNs have been in use since the late 1990’s, and while their popularity has gone up and down, many businesses rely on them to establish reliable communication with remote workers and to maintain close contact with distant partners. Freelancers and individuals with privacy concerns often use VPNs to retain anonymity and increased security on the web.
There are numerous factors to consider when deciding whether or not to use a VPN in your business or organization. The level of security afforded by VPNs is significant – often involving complex data encryption and secure password protection. Earlier VPNs weren’t capable of working with dynamic IP addresses, but this issue seems to have been largely resolved. The use of a dynamic IP with a secure VPN provides an extra measure of protection for data on the network. When connected to wireless networks, however, VPNs can pose a security risk, and additional measures may be required to keep data private.
VPNs are cost-effective and a convenient option for many small business owners, since they require little to no specialized hardware. Installation and maintenance does often require IT professionals with experience in VPNs, though. Reliability can also be an issue. Since VPNs are often remotely contracted, server downtime is not under the user’s direct control. Interoperability may also be a problem. Not all devices and programs for VPNs are compatible, causing a headache for IT professionals maintaining these networks. Problems aside, these networks are fairly flexible, making it easy to add and remove users as needed.
According to TeleworkResearchNetwork.com, the telecommuting workforce has grown by 62% globally and 66% within the United States between 2005 and 2011. This rapid growth presents businesses with significant IT obstacles. Providing workers with the opportunity to telecommute offers organizations significant benefits, but data vulnerability is a serious risk. VPNs are a proven solution to the technological challenges of remote work. The decision to use a VPN should be weighed carefully, but the benefits can’t be overlooked.